Intro
Blockchain technology has given the direction to change the world, but its biggest challenges are – slow speeds, high transaction fees, and limited scalability. Layer 1 blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum are secure but not capable of handling large-scale transactions.
This is where Layer 2 solutions come into play. The main purpose of Layer 2 Blockchain is to make transactions fast, cheap, and scalable, so that the use of blockchain can be easy for ordinary people and large industries.
In this article, we will understand what Layer 2 is, the difference between Layer 1 and Layer 2, its types, popular projects, and the risks associated with it in simple language.
Table of Contents
2 What is Layer 2 blockchain ?
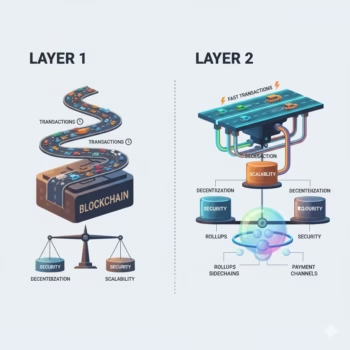
Layer 1 vs Layer 2
Understand the difference between Layer 1 (L1) and Layer 2 (L2) in easy and concise:
| speciality | Layer 1 (L1) | Layer 2 (L2) |
| definition | The main blockchains, such as Bitcoin, Ethereum. | The system built on top of Layer 1 that improves transactions. |
| aim | Providing transaction records, security, and decentralization. | Increasing speed, reducing costs, and improving scalability. |
| Transaction Processing | All transactions are recorded directly on the blockchain. | Most transactions are off-chain processed, with the final result recorded at L1. |
| movement | Slow (because every transaction has to be verified). | Faster (because of off-chain processing). |
| cost | High gas fees (especially on busy networks). | Low cost (less data goes to L1). |
| safeguard | Totally dependent on L1’s own safety. | Uses the protection of L1. |
| example | Bitcoin, Ethereum, Solana. | Lightning Network (Bitcoin), Optimistic/ZK Rollups (Ethereum). |
| Scalability | Limited (fewer transactions per second). | High (can handle thousands of transactions per second). |
| entanglement | Basic and free. | Dependent on L1, additional technology needed. |
Layer 2 work:
The job of Layer 2 (L2) is to make the blockchain (Layer 1) faster, cheaper, and more scalable, so that more people can use it easily. Its main function is the following:
- Increasing Transaction Speed:
- L2 processes transactions outside (off-chain) from the main blockchain (L1), allowing transactions to be completed faster. Example: Bitcoin transactions on the Lightning Network happen in seconds.
- Reducing Costs:
- Gas fees are high to record every transaction on L1. L2 sends less data to L1 by bundling multiple transactions at once, leading to lower fees.
- Enhancing Scalability:
- Limited transactions can be processed per second on L1. L2 can handle thousands of transactions simultaneously, allowing the network to support more users.
- Using L1’s Security:
- L2 does not provide protection on its own, but rather takes advantage of L1’s robust protection. This ensures that transactions remain secure.
- Supporting DApps and Smart Contracts:
- L2 solutions, such as Rollups (Optimistic or ZK-Rollups), make dApps faster and cheaper on blockchains like Ethereum, increasing the use of dApps.
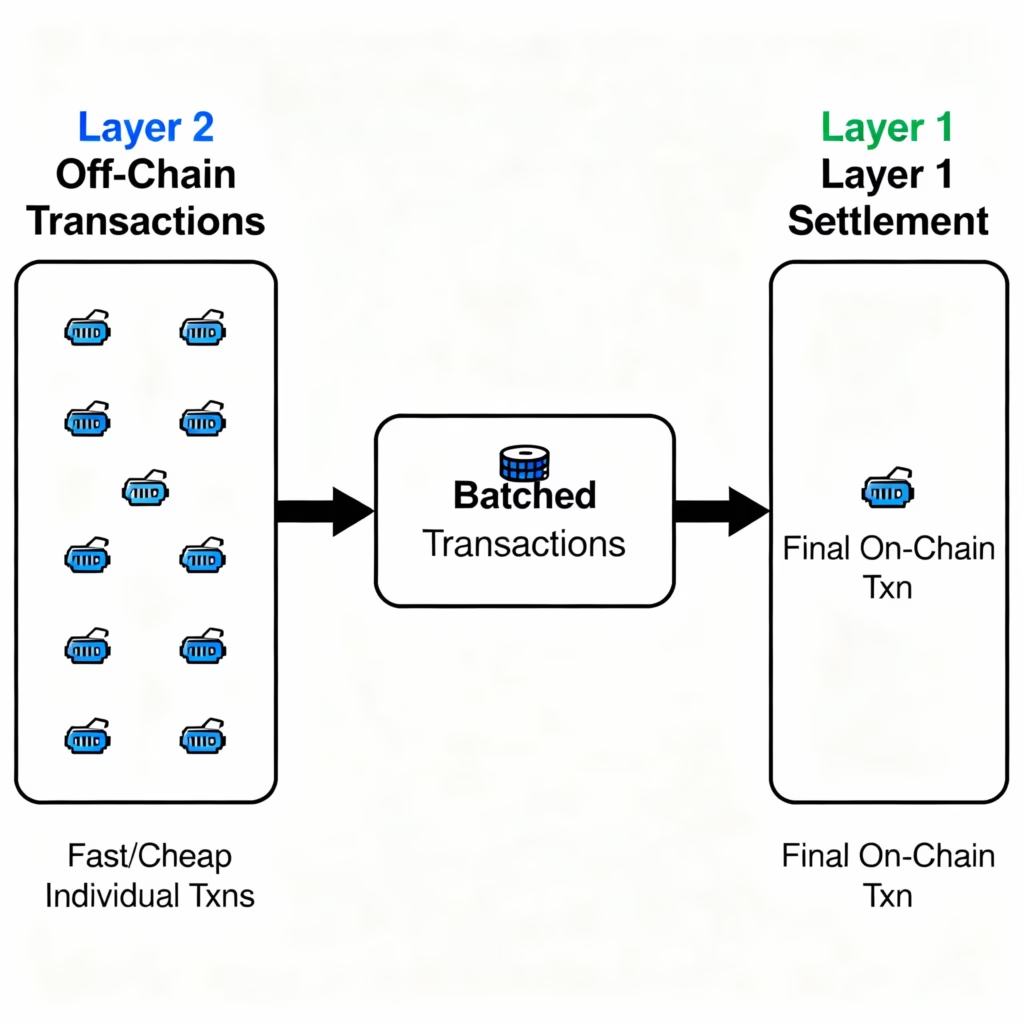
Layer 2 Scaling Solution – Complete process from off-chain transactions to Layer 1 settlement
Understand with Example:
- Suppose you buy coffee every day and it is expensive and slow to record a transaction on the blockchain (L1) every time. On L2 (like the Lightning Network) you do all transactions off-chain and only the final balance is recorded on L1 at the end of the month. This saves time and money.
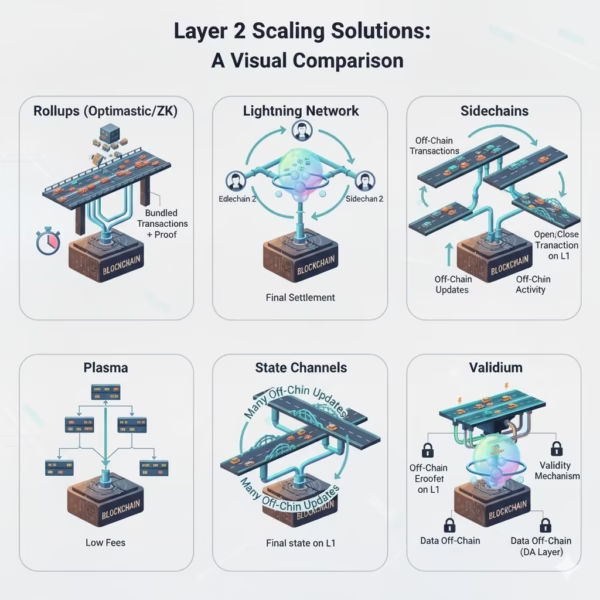
3. Types of Layer 2 Solutions
There are different types of Layer Layer 2 blockchain solutions, designed to improve the scalability, speed, and cost of blockchains (Layer 1). The major types are briefly explained below:
1. Rollups:
- What is?: Process multiple transactions off-chain by “rolling” them together and only record the brief data on Layer 1.
- Type:
- Optimistic Rollups: Assuming transactions are correct, as long as a mistake is proven. Examples: Arbitrum, Optimism.
- Zero-Knowledge Rollups: Verify transactions using cryptography (zero-knowledge proof). Examples: zkSync, StarkNet.
- Advantage: Fast, cheaper, and use layer 1 protection.
- Usage: Popular for Ethereum DApps.
2. Lightning Network:
- What is?:Layer 2 blockchain solution for Bitcoin, which creates off-chain payment channels. Only the final balance is recorded on L1.
- Advantage: Fast and almost free transactions for micropayments.
- Usage: Small transactions of Bitcoin, such as buying coffee.
- Example: Bitcoin Lightning Network.
3. Sidechains:
- What is?: A separate blockchain connected to Layer 1, which processes transactions independently, but shares data from L1.
- Advantage: Fast and flexible, can have different rules and features.
- Disadvantages: May not be as safe as L1.
- Examples: Polygon (although it is now moving towards rollups), Liquid Network.
4. State Channels:
- What is?: Process transactions or smart contracts by opening an off-chain channel between two or more parties. The final position is recorded at L1.
- Advantage: Instant and free transactions, especially for repetitive transactions.
- Usage: Gaming, micropayments, or streaming services.
- Example: Raiden Network (Ethereum), part of the Lightning Network.
5. Plasma:
- What is?: Processes transactions by creating a “child chain” at Layer 1, only the necessary data is sent to L1.
- Advantage: High scalability, low cost.
- Disadvantages: Complex, and users have to check the data from time to time.
- Example: OMG Network (though less prevalent now).
6. Validium:
- What is?: Like ZK-rollups, but the data is stored off-chain, not on L1.
- Advantage: Very high scalability, low cost.
- Disadvantages: Less data availability compared to L1.
- Example: StarkEx, DeversiFi।
Comparison (in a nutshell):
| kind | movement | cost | safeguard | utility |
| Optimistic Rollups | warmth | cheap | Dependent on L1 | DApps, DeFi |
| ZK-Rollups | warmth | cheap | Dependent on L1 | DeFi, NFT, भुगतान |
| Lightning Network | Very Fast | Very affordable | Dependent on L1 | Micropayments (Bitcoin) |
| Sidechain | warmth | cheap | Less secure | General Transactions, DApps |
| State Channels | Very Fast | free | Dependent on L1 | Gaming, streaming |
| plasma | warmth | cheap | medium | Old DApps |
| Validium | Very Fast | cheap | medium | DApps with high throughput |
Popular Layer 2 Projects
Layer 2 blockchain are built to enhance the scalability of projects, solving the speed and cost problems of Layer 1 blockchains such as Ethereum and Bitcoin. These projects provide faster and lower fees by processing transactions off-chain, while maintaining the security of the main blockchain. Below is information on some popular Layer 2 blockchain projects:
1. Polygon
- Description: Polygon, formerly known as Matic Network, is a leading Layer 2 scaling solution for Ethereum. It uses technologies like sidechains and zkRollups.
- Features:
- Capacity for up to 65,000 transactions per second (TPS ).
- Very low transaction fees (about $0.01).
- Suitable for DeFi (Aave, SushiSwap), NFT marketplaces (OpenSea, Rarible) and gaming.
- Interoperability with Ethereum and other blockchains such as BNB Chain.
- Native Token: MATIC (now POL) – Used for gas fees, staking, and governance.
- Pros: Developer-friendly tools and strong DeFi ecosystem.
2. Arbitrum
- Description: Arbitrum is an Optimistic rollup-based Layer 2 solution, enhancing the scalability of Ethereum.
- Features:
- Fast and cheap transactions, almost zero gas fees.
- Widespread use for DeFi (Uniswap, Sushiswap), NFTs, and gaming dApps.
- Full compatibility with EVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine).
- Native Token: ARB
- Pros: Strong developer community and support for over 300 dApps.
3. Optimism
- Description: It is also an optimistic rollup solution, which makes Ethereum transactions faster and cheaper.
- Features:
- Superchain architecture, which integrates multiple Layer 2 chains.
- Average transaction fee less than $0.1.
- Support for DeFi projects like Synthetix and 30+ superchain networks (e.g. Base, Lisk).
- Native Token: OP
- Advantages: Easy tools and open-source ecosystem for developers.
4. zkSync (ZKSYNC)
- Description: zkSync is a ZK-Rollup based Layer 2 solution, emphasizing privacy and security.
- Features:
- Fast and secure transactions with zero-knowledge proofs.
- Suitable for micropayments and large-scale token transfers.
- Scalability with Ethereum’s security.
- Native Token: ZK
- Advantages: Popular for DeFi and mass token transfers.
5. Immutable X
- Description: This is a Layer 2 blockchain solution designed specifically for NFTs and gaming, which uses zk-Rollups.
- Features:
- Gas-free NFT minting and trading.
- More than 9,000 transactions per second.
- Supporting gaming projects like Gods Unchained and Illuvium.
- Native Token: IMX
- Advantages: Eco-friendly and ideal for the gaming/NFT ecosystem.
6. Mantle
- Description: Mantle is an EVM-compatible Layer 2 blockchain solution, built for Web3 gaming and the metaverse.
- Features:
- 4,000 TPS and a TVL of $204.83 million.
- Support for 250+ dApps, especially in gaming and DeFi.
- Cross-chain interoperability.
- Native Token: MNT
- Advantages: DAO-governed and developer-friendly.
7. StarkNet
- Description: This is a ZK-Rollup based Layer 2 solution, which uses STARK Proofs.
- Features:
- Zero-knowledge proofs for privacy and security.
- Capacity up to 857 TPS.
- Market cap of $345 million.
- Native Token: STRK
- Advantages: Suitable for complex smart contracts and DeFi projects.
8. Loopring
- Description: Loopring is a ZK-Rollup based Layer 2 protocol, known for high-performance DEXs (Decentralized Exchanges).
- Features:
- 2,000+ transactions per second.
- Very low gas fees (less than a cent).
- Ring-matching and fast trading with zkRollups.
- Native Token: LRC
- Advantages: Fast and cost-effective for DeFi and trading.
9. Shibarium
- Description: This is a Layer 2 blockchain solution built for the Shiba Inu ecosystem, which is based on Ethereum.
- Features:
- Fast and cheap transactions.
- Support for the SHIB metaverse and stablecoin SHI.
- Suitable for DeFi and NFTs.
- Native Tokens: SHIB, LEASH, BONE
- Benefits: Community-inspired and useful for the metaverse.
10. Lightning Network
- Description: This is a Layer 2 blockchain solution for Bitcoin, designed for microtransactions.
- Features:
- Possibility of millions of transactions per second.
- Instant transactions with very low fees.
- Use of off-chain payment channels.
- Advantages: Crucial for Bitcoin’s scalability.
4. Why Layer 2 Blockchain Matters?
Layer 2 blockchain projects are crucial for solving problems related to the scalability, speed, and cost of technology. These projects overcome the limitations of major blockchains (Layer 1) such as Ethereum and Bitcoin, making the use of blockchain more efficient, cheaper, and possible on a larger scale. Below explains why Layer 2 Blockchain is important:
1. Improving scalability
- Problem: Layer 1 blockchains, such as Ethereum, can process limited transactions per second (TPS) (Ethereum: ~15-30 TPS). This leads to network congestion and delays.
- Layer 2 blockchain Solutions: Layer 2 projects (such as Polygon, Arbitrum) process transactions off-chain, enabling thousands or millions of TPS. For example, Polygon supports up to 65,000 TPS. This makes the blockchain suitable for large-scale use, such as DeFi, gaming, and NFT marketplaces.
2. Low transaction fees
- Problem: Gas fees (transaction costs) can be very high on Layer 1, especially on Ethereum, where a simple transfer can cost anywhere from $10-$100.
- Layer 2 Solutions: Layer 2 solutions like Optimism, zkSync, and Loopring reduce transaction fees by less than one cent. This makes the use of micropayments, everyday transactions, and DeFi protocols affordable.
3. Use of the security of the main blockchain
- Layer 2 blockchain projects process off-chain transactions, but their security is derived from Layer 1 (such as Ethereum).
- For example, rollups like Arbitrum and zkSync bundle and record transactions on Layer 1, retaining Layer 1’s robust security and decentralization. It offers the perfect blend of reliability and scalability.
4. Support for DeFi and dApps
- Layer 2 blockchain projects provide fast and affordable platforms for decentralized applications (dApps) like DeFi (Decentralized Finance), NFTs, and gaming.
- Example: Immutable X offers gas-free NFT minting and trading, ideal for gaming and NFT marketplaces. Similarly, DeFi protocols like Uniswap and Aave run on Arbitrum and Optimism, providing users with low-cost trading and lending.
5. Environmentally friendly
- Layer 1 blockchains, especially those based on Proof-of-Work (PoW) (such as older Ethereum or Bitcoin), consume a lot of energy.
- Layer 2 blockchain solutions reduce energy consumption due to off-chain processing, making them more environmentally friendly. For example, zkRollups and Optimistic Rollups use fewer computational resources.
6. Large-scale use of blockchain
- Layer 2 blockchain solutions prepare blockchains for mass adoption (mass acceptance).
- Due to fast transactions and low costs, Layer 2 enables everyday uses such as micropayments, online gaming, and cross-border payments. For example, Bitcoin’ s Lightning Network is ideal for micropayments, such as buying coffee.
7. Interoperability and Cross-Chain Solutions
- Many Layer 2 blockchain projects (such as Polygon and Mantle) offer interoperability between different blockchains, facilitating the exchange of data and value between different networks.
- This makes the Web3 ecosystem more integrated and user-friendly.
8. Developer-Friendly Ecosystem
- Layer 2 blockchain projects provide developers with Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) compatible tools and frameworks, making it easy to create dApps.
- For example, Arbitrum and Optimism are EVM-compatible, allowing developers to migrate their Ethereum dApps to Layer 2 blockchain without much change.
5. Risks & Challenges
Layer 2 projects are crucial in solving the scalability and cost problems of blockchain, but they also come with several risks and challenges. Below is a detailed explanation of the key risks and challenges related toLayer 2 blockchain solutions:
1. Security Risks
- Description: AlthoughLayer 2 blockchain solutions use the security of Layer 1 (such as Ethereum), their smart contracts may have vulnerabilities.
- Example: Optimistic rollups have the potential for fraud during the “Challenge Period” if an attacker submits incorrect data.
- zkRollups may be prone to bugs or hacking due to complex cryptography (Zero-Knowledge Proofs).
- Impact: Users’ funds may be stolen or dApps may be disturbed. For example, in 2022, there were cases of smart contract hacks in some Layer 2 projects.
- Solution: Developers should pay attention to code audits and bug bounty programs.
2. Centralization Risk
- Description: Some Layer 2 blockchain solutions, such as sidechains or some rollups, may rely on centralized nodes or operators.
- Example: Polygon’s PoS (Proof of Stake) network has a limited number of validators, pointing to centralization.
- Impact: If there is control over certain nodes or operators, it can undermine the principle of decentralization and increase the risk of censorship or data manipulation.
- Solution: The need for more decentralized validator networks and transparent governance models.
3. Interoperability Challenges
- Description: Different Layer 2 blockchain projects use different technologies (e.g. zkRollups, Optimistic Rollups), which may not be fully compatible with each other.
- Example: Data or token transfers between Arbitrum and Optimism require a complex bridging process.
- Impact: Users may face complex processes and additional fees, affecting the user experience.
- Solution: Cross-chain bridges and standardized protocols are in the works, such as Polygon ‘s AggLayer.
4. Bridging Risks
- Description: Bridges are used for token transfers between Layer 2 blockchain and Layer 1 blockchain which can become targets for hacking.
- Example: In 2022 , the bridge hack of Ronin Network (which is a sidechain) occurred, with over $600 million stolen.
- Impact: Users may lose their funds, and trust in Bridges may diminish.
- Solution: Multi-signature bridges, better audits, and the need for decentralized bridging solutions.
5. Data Availability Issues
- Description: Some Layer 2 blockchain solutions, such as Optimistic Rollups, rely on Layer 1 for data availability. If the Layer 1 blockchain network is congested, Layer 2 transactions may be affected.
- Impact: Transaction speed and cost can be affected, especially during high network traffic.
- Solutions: Data availability solutions like Celestia or upgrades like Ethereum ‘s Danksharding are in the works.
6. User Experience Complexity
- Description: Using Layer 2 networks can be complex for new users. Such as, bridging, wallet configuration, and switching between different networks.
- Example: To transfer funds to Arbitrum or zkSync the user has to add a network to MetaMask and use Bridge.
- Impact: Complex processes can prevent mass adoption, as common users want a simpler experience.
- Solution: Focus on user-friendly wallets and onboarding tools.
7. Regulatory Risks
- Description: Crypto and blockchain projects are under increasing regulatory scrutiny globally. Layer 2 projects, particularly those involving DeFi and NFTs, may face regulatory actions.
- Example: In some countries, non-compliance with KYC/AML regulations may result in sanctions on projects.
- Impact: Projects may have a halt in operations or a drop in the token value.
- Solution: Focus on regulatory compliance and transparent operations.
8. Token Price Volatility
- Description: Native tokens of Layer 2 projects (such as MATIC, ARB, OP) are affected by the volatility of the crypto market.
- Example: Tokens like Polygon (MATIC) or Arbitrum (ARB) saw a significant drop in value during the market crash.
- Impact: The risk for investors increases, and the volatility of the token for gas fees can affect users.
- Solution: Invest only what you’re willing to lose, and go for a long-term strategy.
9. Developer and Community Dependency
- Description: The success of Layer 2 projects depends on the developer community and building dApps. If developers abandon the project, its ecosystem may be weakened.
- Example: Some small Layer 2 projects failed due to lack of developer support.
- Impact: Project usage and token value may be affected.
- Solution: The need for strong developer incentives and community engagement.
10. Technical Complexity and Upgrade Risks
- Description: Layer 2 projects involve complex technologies such as zkRollups and Optimistic Rollups, which can lead to mistakes in upgrades or maintenance.
- Example: An incorrect upgrade can lead to network downtime or data loss.
- Impact: User trust and network stability can be affected.
- Solution: Rigorous testing and decentralized governance models.
Conclusion
Layer 2 Solutions is the backbone of the future of blockchain. These multiply transaction speed and scalability while maintaining the security of the Layer 1 blockchain. Projects like Polygon, Arbitrum, Optimism, and Lightning Network have already shown how Layer 2 can prepare blockchain for everyday life and mass adoption.
However, with these comes some security, centralization, and bridging risks, but continuous technological improvements and a strong developer community are overcoming these challenges.
If blockchain is to unlock its true potential, Layer 2 solutions are going to play the most important role.